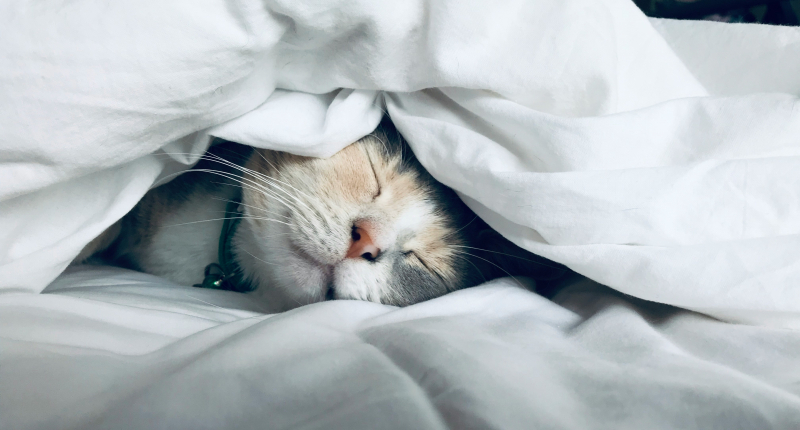
It’s been said over and over again: sleep is crucial to our well-being. Not only does it help our bones grow, but it also consolidates memory and cognitive function while improving energy levels. However, there is a deeper layer to how your sleep works.
Sleep cycles are key to understanding both the process and the quality of our sleep. There are four stages of sleep, which fit into two categories known as NREM (Non-Rapid Eye Movement) and REM (Rapid Eye Movement).
- NREM – Falling Asleep
This is the stage when you first begin falling asleep. Most of the time, you won’t even notice it happening. This is the stage where your body prepares itself for processes such as repairing and recovering from injuries. If you happened to wake up during this stage, you wouldn’t even know that you’d been sleeping at all.
Your muscles begin to relax, along with the rest of your body. Your eyes usually slide around under the eyelids, getting used to the feeling. Both your heart rate and breathing start to slow down.
- NREM – Light Sleep
Light sleep is the stage we spend the most time in while sleeping. Your body temperature begins to drop, and there is no eye movement. Furthermore, your heart rate and breathing slow down even more. Your body is preparing itself for the next stage – deep sleep.
During the Light Sleep stage, your brain begins to do something that is called
‘sleep spindles’. Sleep spindles are a specific brain pattern that isn’t fully understood by researchers. However, what we do know is that during the sleep spindles phenomenon, the brain processes your day and logs it into your memory. Researchers believe that it may also help with motor skills, especially around our fingers.
Additionally, there is something else that happens, like sleep spindles, K-complexes are a series of brainwaves. In the most simple terms, it’s basically a series of brainwaves that help the brain to relax and quietens alertness levels. It helps to tell our brains that the environment is safe, and we are able to sleep.
These are very complicated neurological concepts I can’t fully understand. Please contact your local bio-physics teacher to help.
- REM stage
To make it simple, there are two REM stages:
Most people think REM is simply the sleep stage where your eyes move around a lot. while this is true, it’s specifically only phasic REM where the eye movement happens.
There is Phasic, and then there’s Tonic.
REM is the sleep stage where your eyes move around a lot – and is also known as the ‘dreaming’ stage. While those facts are true, only phasic REM is when your eyes move around a lot.
And yes, during this time your brain activity begins to peak. Dreaming begins to happen, and your breathing and heart rate will increase. Your muscles stop moving. External muscles are paralysed while internal muscles and structures become activated, but sometimes small twitches can still occur.
- NREM – Deep sleep
Deep sleep is when the real recovery happens. This is the stage where the body begins the process of repair and growth. Things such as things such as cell and tissue regeneration, as well as recovery from any illnesses or injuries can finally occur. This is the ‘heaviest’, or deepest stage of sleep. It’s very hard to wake someone up if they’re going through the NREM deep sleep stage.
Note that your body is completely relaxed during all this. there is no eye movement whatsoever, and your heart rate and breathing reach and all time low. Your immune system is strengthening again.
Well, there you have it! The main four components of sleep. All of these are equally as important as the next, but if you’re sick, deep sleep is the most significant one. For us as students, sleep is crucial for retaining information and studying. All-nighters aren’t as helpful as you would imagine them to be.
Happy sleeping!
6th May, 2024
Written by Emma Li, edited by Aaron Huang and Hope Zhang
Photo by Kate Stone Matheson on Unsplash